- Main page
- News
Railway digital model
4/18/2022
Monitoring the state of the track, facilities and repair work requires the creation of reference systems for monitoring the plan and profile of the track on the country's railways. Employees of the Center for Space Research and Remote Sensing of the Earth of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University offer their services to railway workers - the creation of an electronic map based on space images of medium spatial resolution, a database of communications and a geoportal of railway communications.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a successfully developing information technology that is effectively used in many industries, including transport. At the same time, transport GIS has one important feature - the widest range of users who need transport information. These are the transport workers themselves, that is, those who build and maintain the transport infrastructure in working condition. These are those who carry out transportation by transport. This includes passengers, as they use transport to travel. And everyone: ordinary passengers, transport infrastructure maintenance professionals and carriers need information about transport networks and facilities. Indeed, everyone needs maps of railways and roads, and transport schemes for large areas.
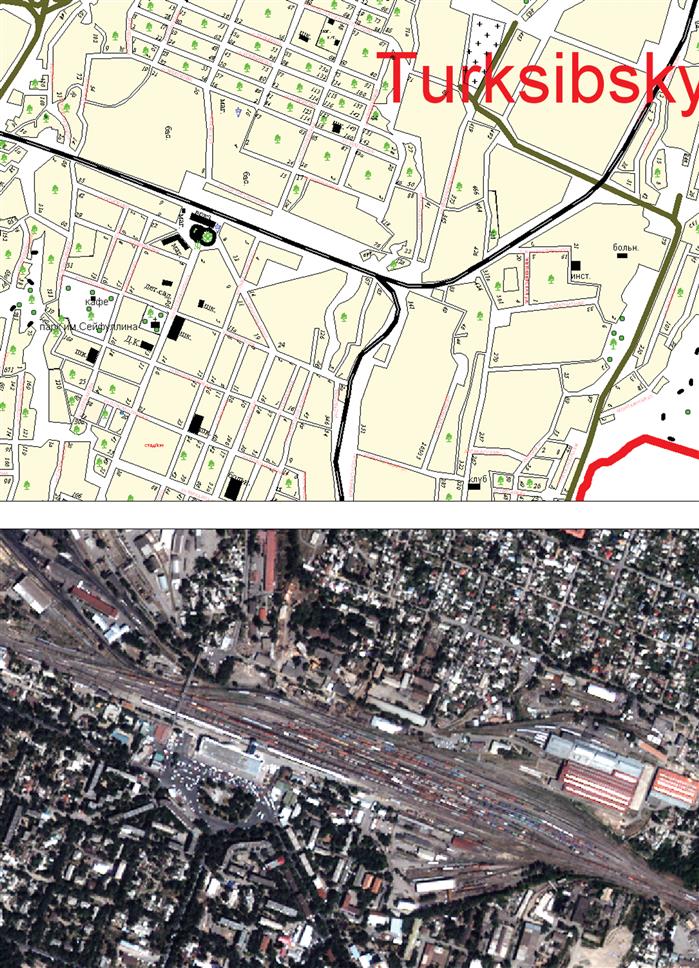
According to the director of the Center for Remote Sensing of the Earth of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University Bakhyt Sakhariev, passengers, carriers and transport infrastructure providers need information about objects and transport networks. For example, private railway companies are controlled by the Transport Committee. For them, the e-card is very useful. It allows you to see every centimeter of the railway. It is difficult to say that the current cards fully meet modern requirements. The geographic information system, provided in the form of a model of railways, currently forms the basis of any production activity of an enterprise in this area.
At the moment, JSC NC "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" does not have technical and software resources that would allow to quickly carry out work on digitization in absolute geographical coordinates of the plan and profile of the railway, track development schemes and technical plans of stations, the location of signaling devices, engineering -technical structures and other facilities. They only have a raster map in their hands, that is, a scanned copy of the map. The currently existing data on the plan and profile of the railways, presented on paper, need to be re digitize due to the fact that many sections of the railway have undergone changes. They are not reflected in the plans and profiles stored in paper form, and cannot form the basis for the creation of electronic maps.

The basis of the activity of any enterprise is made up of models of the main technological objects and processes, to which the main production activity is directed. For Joint Stock Company “National Company “Kazakhstan Temir Zholy”, in particular for the Department of Tracks and Structures, the main object of production activity is railways, including plans and profiles of railway tracks, track development schemes and technical plans of stations and spans, signaling and communications, various engineering and technical facilities and other facilities.
Employees of the Center for Space Research and Remote Sensing of the Earth of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University have experience in developing a GIS of communication routes, the necessary software and hardware resources, offer the creation of a GIS railway in three stages:
Stage 1. Creation of an electronic map based on space images of medium spatial resolution (6 - 16 m / pxl), creation of a database of communication routes, creation of a geoportal of railway communication.
Stage 2. Creation of an electronic map based on satellite images of high spatial resolution (0.5 - 2 m / pxl), collection of data on infrastructure along railway lines, creation of a database of infrastructure objects along railway lines, updating the geoportal of railway lines.
Stage 3. Creation of an integrated geographic information system for monitoring the health and safety of railway lines of communication in the Republic of Kazakhstan. Development of a system for monitoring the condition of rail tracks and sleepers. Development of a monitoring system for railway crossings and light indicators (semaphores). Adding semantic information about the objects of the command and control system to the spatial database of the railway communication paths. Development and integration into the interface of the geoportal of analysis functions and visual warnings. Connection to the interface and to the geodatabase of security certificates of public and private railway sections.
As the world experience in the field of railway operation shows, the basis of the production activity of any private or state railway enterprise is currently a detailed model of railways, usually presented in the form of a geographic information system, which is the basis for operational, current and long-term planning and design of railway works.
According to the head of the center, in order to solve the problem of creating, implementing and operational technical and software support and maintenance of an electronic map of the railways of the Republic of Kazakhstan, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
- design and development of technical means that allow for the rapid digitization of the railway network of the Republic of Kazakhstan in absolute geographical coordinates;
- development of a software and hardware complex (STC) for automated digitization of the main railway network of JSC NC "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" based on satellite navigation technology (for example, using the "DMTS GPS Scanner" STC);
- industrial implementation of PTK in JSC NC "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" and work on digitization of the railway network in order to create a digital model of the main railway network of the Republic of Kazakhstan using remote sensing data;
- selection of software tools for creating and maintaining an electronic map of the main network, railways of the Republic of Kazakhstan and using the obtained data on digitization to fill it;
- combining, within the framework of a single electronic map of the main network of railways of the Republic of Kazakhstan, according to the totality of databases of the transportation process, and first of all, the plan and profile database with the RSHBK database (rail-sleeper-ballast map).
The project proposed for implementation allows solving the first two tasks:
- design and development of technical means that allow for the rapid digitization of the railway network of the Republic of Kazakhstan in absolute geographical coordinates;
- development of a software and hardware complex for automated digitization of the main railway network of JSC NC "Kazakhstan Temir Zholy" based on satellite navigation technology.
An analysis of existing and developed abroad hardware and software complex for monitoring railways based on satellite navigation technology shows that this is the main, and often the only way to create and operationally support electronic maps of the railway network for solving special problems.
There are several ways to solve this problem on the way of creating and operational support of an electronic map:
- use of foreign hardware and software complex for monitoring the railway based on GPS technology;
- the use of other technologies for creating an electronic map of the railway network (aerial photography or space photography with subsequent vectorization of the railway network);
- development and creation of hardware and software complex for monitoring the railway based on geodetic methods using GPS technologies by domestic firms and specialists.
GIS software tools are quite flexible and diverse. Roads and road facilities are very complex and expensive technical structures that require constant monitoring and consideration of their main characteristics. Naturally, in the process of certification, diagnostics and other works, a huge amount of heterogeneous information is accumulated that needs to be systematized and analyzed. In this complex problem, information systems based on modern computer technologies, in particular DBMS and GIS, should be of great help.
The creation of a single information space implies the development of a wide range of interconnected processes and systems. These promising and efficient technologies allow solving many different applied problems, in particular, the digitalization of logic and the analysis of objects and resources of message paths.
- The main tasks of management, solved with the help of GIS, are: flow management, management of transport infrastructure facilities, management of real estate objects of transport infrastructure, maintaining a cadastre of transport facilities, ensuring traffic safety, making decisions in emergency situations, etc.
The use of GIS allows you to optimize many aspects of transport activities. GIS not only allows you to integrate heterogeneous information into a single information environment, but also provides a variety of visualization tools. Most often, the end result is a presentation of data in the form of a map or graph. Over time, using space images, you can track the railways along their entire length and make changes. The electronic map has a database. You can add the entire infrastructure around the railway, including railway stations and crossings, it is not difficult to register every detail on the map - from the semaphore to the sleepers. The possibilities of modern space technologies allow this. Satellites of the USA, France, China can take photographs, where 1 m / sq. fits into 1 pixel. In this case, we can see each sleeper in real time. When compiling an electronic map, we use not only images taken from space. In some areas we use drones or a laser, we combine the results and make a complex electronic system. For example, a worker discovers a railroad defect and immediately enters it into an electronic map on a tablet. Next, the dispatcher sends a message to the situational center, - explains the director of the Center for Remote Sensing of the Earth of Al-Farabi Kazakh National University Bakhyt Sakhariev.
Kairzhan TUREZHANOV

